Description:
privacyIDEA Authenticator for Android version 4.3.0 allows recovery of enrolled OTP/TOTP/HOTP secret seeds through runtime hooking of cryptographic functions. On a rooted device, a local attacker can attach an instrumentation framework (such as Frida) to the app process and intercept cryptographic operations. During decryption routines, plaintext OTP seeds are present in memory and can be read directly from process buffers. This exposure enables an attacker with local privileged access to extract enrolled OTP seeds and generate valid one-time passwords for associated accounts, effectively bypassing two-factor authentication once the device is compromised.
Impact:
Local privilege → OTP seed disclosure → valid OTP generation → potential 2FA bypass.
Attack prerequisites:
Attacker must have root or equivalent local code-execution privileges on the target device to inject runtime hooks.
Affected versions:
privacyIDEA Authenticator 4.3.0 (tested on Android 11).
No fixed version was available at the time of analysis.
Mitigation:
Treat a rooted or otherwise compromised device as untrusted. Enforce device-integrity checks (e.g., MDM or Play Integrity API). For stronger protection, use hardware-backed, non-exportable keys or external tokens to store OTP secrets and limit plaintext exposure in memory.
CWE:
- CWE-922 – Insecure Storage of Sensitive Information
- CWE-522 – Insufficiently Protected Credentials
- CWE-200 – Exposure of Sensitive Information to an Unauthorized Actor
PoC:
Install/start Frida or equivalent hooking tool (or malware that performs equivalent hooking).
Launch or attach to the privacyIDEA Authenticator process (it.netknights.piauthenticator).
Inject a tracer script (or equivalent, not showed here) that hooks the crypto functions and captures plaintext buffers when the app accesses or decrypts stored seeds.
Dump the plaintext seeds and exfiltrate them to the attacker.
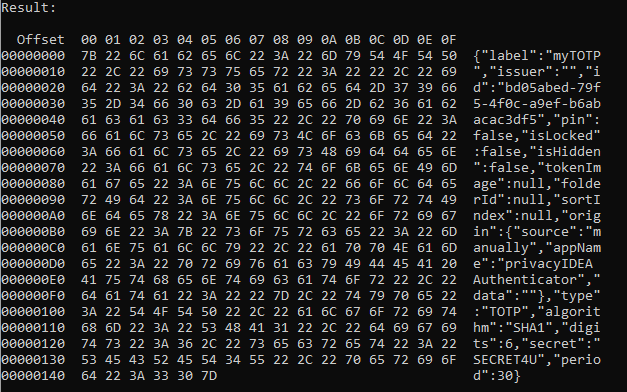
The PoC recovers seeds after enrollment and after the app was closed, showing persistent storage secrets are retrievable once an attacker can instrument the process. The attack does not require the app to be actively displaying the QR or to be in the enrollment UI when secrets are extracted.
Suggested CVSS v3.1 vector (base):AV:L/AC:H/PR:H/UI:N/S:C/C:H/I:H/A:N = 6.8
Suggested CVSS v4.0 vector (base, approximate):AV:L/AC:H/PR:H/UI:N/S:C/C:H/I:H/A:N ≈ 6.6
Attack Vector (AV): Local (L) — attacker must run code on the device.
Attack Complexity (AC): High (H) — successful exploitation requires a compromised device + runtime instrumentation knowledge.
Privileges Required (PR): High (H) — attacker needs high privileges (root) to inject Frida into the process in typical Android configurations.
User Interaction (UI): None (N) — once the device is compromised, no further user interaction is required.
Scope (S): Changed (C) — confidentiality loss of secrets can lead to takeover of external accounts/services (impact crosses component boundary).
Confidentiality (C): High (H) — complete disclosure of OTP/TOTP/HOTP seeds.
Integrity (I): High (H) — an attacker can generate valid OTPs (logical integrity of 2FA compromised).
Availability (A): None (N) — the vulnerability does not directly affect availability.
Credits:
Discovered by Oliver and Philippe.
References:
DIVA research paper (proof-of-concept and analysis):
https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/record.jsf?pid=diva2%3A1880460&dswid=5771
DIVA research paper PDF:
https://www.diva-portal.org/smash/get/diva2:1880460/FULLTEXT01.pdf
// Oliver

Lämna ett svar